Will cars of the future lack drivers?
This may be the year the automotive industry transforms itself into the personal robot industry, at least at the International CES trade show in Las Vegas this month.
Nine out of 10 of the largest international automotive manufacturers displayed multiple technological innovations that included electric motor drive systems, fuel cell and solar power integration, wireless recharging stations, 4G LTE mobile connectivity, an abundance of sensors, intelligent suspension systems, lightweight composite materials, expanding apps, and for the first time — autonomous vehicles.
The Driverless Car Experience at the Gold Pavilion was extraordinary. In 2011, Nevada became the first state to legally allow autonomous vehicles to operate on its roadways. If a startup company called Induct has its way, downtown Las Vegas residents may soon be riding in the first autonomous vehicles operated in the country. The company’s NAVIA autonomous trolleys are “100 percent electric and 100 percent driverless.”
The platform navigates streets by using GPS mapping and lidar sensors to detect the distance, shape and height of any obstacles near it. The batteries that provide energy for the electric drive system are recharged at wireless inductive charging stations that can be installed at key points along the trolley route.
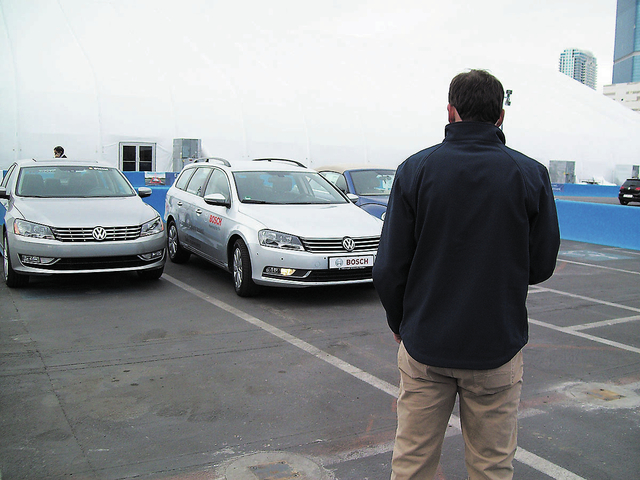
Bosch Automotive and Valeo also showcased remote autonomous parking and automatic emergency braking technologies installed on Volkswagen vehicles.
Someday soon, a family might arrive at a local shopping mall, exit their car in front of their favorite store, and then use an app on their hand-held mobile device to instruct the vehicle to remotely park itself, while monitoring an onboard camera as it completes its objective.
The Bosch/Valeo platform used eight ultrasonic sensors and four near-range cameras to maneuver the vehicle between two other parked cars while the driver stood outside the vehicle 15 feet away.
Bosch bought Evatran, a company that provides wireless recharging systems for the Chevrolet Volt and Nissan LEAF. Bosch displayed that technology in the North Hall of the Las Vegas Convention Center, alongside its standard SAE J1772 wired charging stations.
Qualcomm, the world leader in developing 3G and 4G LTE wireless communication technology, is promoting the Halo wireless inductive charging system for electric cars. Qualcomm is one of the corporate sponsors for the new Formula E international electric racing series, sanctioned by the Federation Internationale de l’Automobile. Formula E will kick off its inaugural season in September in Beijing. Ten racing teams will compete around the world, including Los Angeles and Miami. Racing team sponsors include the Andretti family. Richard Branson and Leonardo di Caprio.
Qualcomm will provide its Halo inductive charging system as part of the event support infrastructure, with the long-term goal of enabling the electric race cars to recharge wirelessly from the track itself while the vehicles are moving. A Spark-Renault Formula E electric race car was displayed at the Qualcomm booth in the Central Hall. A Qualcomm press conference at Mandalay Bay featured Formula 1 racecar driver Lucas di Grassi spinning doughnuts in the parking lot. The Spark-Renault car can exceed speeds of 150 mph and accelerate from zero to 60 mph in just seconds. Other automotive industry sponsors of the Formula E racing series include McLaren, Michelin and Tag Heuer.
Ford Motor Co. exhibited a unique concept for one of its C-Max Energi cars that featured solar cells embedded on top of the vehicle body. While parked in an east-west direction under an oversized parking facility, a fresnel lens solar collector concentrates the ambient light from the sun to the solar cells and increases the battery recharging capacity by eight times, allowing the C-Max Energi plug-in hybrid to be recharged up to 8 kilowatt-hours during a full day of sunshine. While parked in “sleep mode.” The C-Max Energi could autonomously sense and position itself within the parking space and under the fresnel lens to track the movement of the sun and optimize solar collection by the cells.
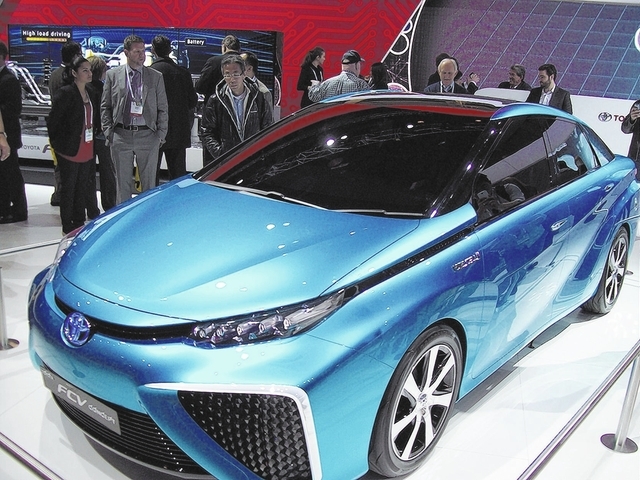
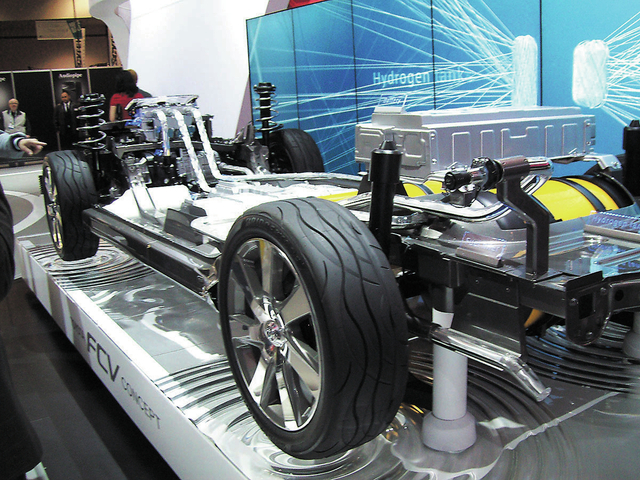
Toyota has been the leader in commercializing hybrid gasoline/electric platforms and is taking the lead to introduce a hydrogen fuel cell/electric-drive platform as well as a unique three-wheel electric car that will be manufactured in 2015. Toyota’s stunning FCV concept vehicle has a unique shape the purposely ducts large amounts of air from the front of the vehicle into and under its chassis to provide oxygen that mixes with two onboard tanks of compressed hydrogen gas.
The fuel cell creates electricity to drive its electric motor and forms water vapor at its exhaust pipe. With a range of 300 miles, a top speed of 105 mph and the torque of an electric motor drive train, this platform can usher in another automotive technology revolution. Toyota executives acknowledged a lack of hydrogen refueling station infrastructure worldwide, but are looking to California as its initial U.S. marketplace, where that state is already installing hydrogen stations at key locations.
The Toyota i-ROAD is an enclosed three-wheel electric car that can seat two passengers in tandem. The little car features an “Active Lean” intelligent suspension system. The rear wheel drives and steers, while the front two wheels and vehicle suspension are actively controlled by an onboard computer that monitors three gyroscopes, accelerometers and wheel encoder sensors. Slower speeds allow for a tighter turning radius while faster speeds create a wider radius that can be offset by the vehicle’s ability to lean into turns. The driver experience is similar to flying in three dimensions, rather than just two.
BMW unveiled its 2014 model i3 electric car by shipping in 25 vehicles to International CES for testdrives by attendees at the Las Vegas Convention Center. The i3 has lots of torque and acceleration from its electric motor, with a range of 100 miles after each charge. An optional gasoline-powered range extender can supplement the battery pack to exceed 240 miles between refueling stops.
ChargePoint, an electric vehicle supply equipment manufacturer from California, is integrating a locator map service with the i3 GPS navigation system to help the driver find nearby charging stations. If the stations are part of the ChargePoint wireless network, the service can provide information about real time usage when a driver is choosing a nearby location site to recharge.
Cameras are everywhere on today’s vehicles. Go Pro, Cobra Electronics, iON and Midland offer products that combine cameras with GPS systems to record, play back and share driving experiences with social media connections. GM announced its Performance Data Recorder feature that will embed this capability into GM vehicles.
GM will also be embedding 4G LTE wireless connections on 10 of its 2015 model cars, including the Corvette, Chevrolet Volt and Chevrolet Spark EV. A GM car becomes a mobile “hot spot” whose passengers can connect seven devices to high-speed applications.
Today’s mobile robots hide their sensors, integrated circuits, miles of wires, and millions of lines of software code in beautiful, streamlined platforms that can morph quickly to meet the needs of their drivers and passengers on demand.
The age of mobile robots has just begun.
Stan Hanel has worked in the electronics industry for more than 30 years and is a longtime member of the Electric Auto Association and the Las Vegas Electric Vehicle Association. Hanel writes and edits for EAA’s “Current Events” and LVEVA’s “Watts Happening” newsletters. Contact him at stanhanel@aol.com.